Python comparison operators are used to compare two values or expressions. These operators return a boolean value (True or False) based on the result of the comparison. Here’s an overview of the comparison operators in Python along with examples:
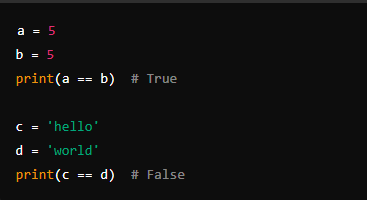
1. Equal (==)
- Description: Checks if two values are equal.
- Example:
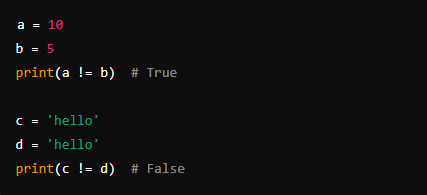
2. Not Equal (!=)
- Description: Checks if two values are not equal.
- Example:
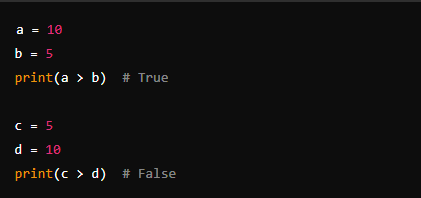
3. Greater Than (>)
- Description: Checks if the value on the left is greater than the value on the right.
- Example:
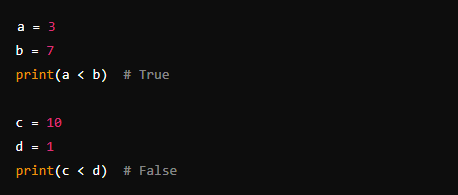
4. Less Than (<)
- Description: Checks if the value on the left is less than the value on the right.
- Example:
5. Greater Than or Equal To (>=)
- Description: Checks if the value on the left is greater than or equal to the value on the right.
- Example:

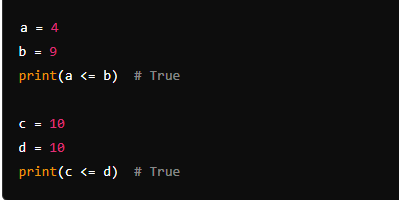
6. Less Than or Equal To (<=)
- Description: Checks if the value on the left is less than or equal to the value on the right.
- Example:
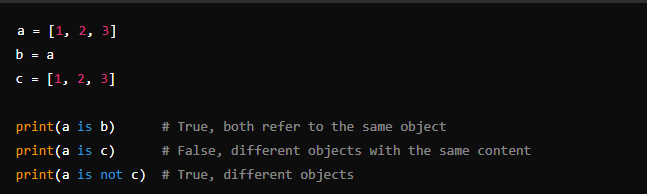
7. Identity Operators (is, is not)
- Description: These operators are used to check if two variables refer to the same object in memory.
- Examples:
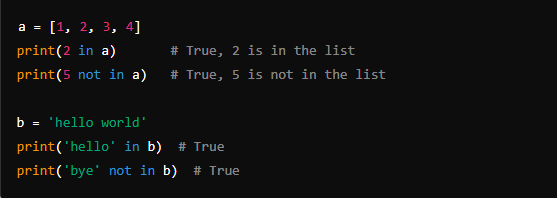
8. Membership Operators (in, not in)
- Description: Used to check if a value exists within a sequence (like a list, tuple, string).
- Examples:
Post Views: 65
