Python ChatBot (Basic)
Functioning and Tools Used in the Chatbot Project
This project aims to create a simple Python chatbot that answers Python-related questions using a graphical user interface (GUI). It is designed for students and beginners who want to understand how Python’s GUI capabilities work with basic programming logic.
Functioning of the Chatbot
User Interaction:
- The chatbot starts with a welcome message, introducing itself to the user.
- The user enters a question related to Python programming in the input box.
Processing the Input:
- The user’s question is captured and passed to the
get_responsefunction. - This function checks if the input matches one of the predefined questions stored in a dictionary.
- The user’s question is captured and passed to the
Generating a Response:
- If the question is found in the dictionary, the chatbot retrieves the corresponding answer.
- If the question is not recognized, the chatbot responds with a default message like, “I’m sorry, I don’t know the answer to that question.”
Displaying the Response:
- The user’s question and the chatbot’s response are displayed in a scrollable text window, maintaining a history of the conversation.
Continuous Interaction:
- The chatbot continues to process and respond to each new input from the user.
Tools Used
This project primarily uses the following Python libraries and tools:
tkinter:- A built-in Python library for creating GUIs.
- Used to design the chatbot interface, including:
- A scrollable chat window for conversation history.
- An input field for the user to type questions.
- A button to send the user’s message.
Python Dictionaries:
- Used to store predefined questions and their corresponding answers.
- Serves as the chatbot’s knowledge base.
ScrolledText:- A widget in
tkinterthat allows the chat window to be scrollable. - Essential for displaying long conversations without cluttering the interface.
- A widget in
Control Flow Logic:
- Simple
if-elsechecks are used to match user input with the predefined questions. - Provides the logic for fetching and displaying appropriate responses.
- Simple
Description for Students
This chatbot project demonstrates how to create an interactive Python application with a graphical user interface. It combines key programming concepts such as:
- Data Structures (Dictionaries): Learn how to store and retrieve data efficiently.
- GUI Programming: Understand the basics of building user-friendly interfaces with
tkinter. - Event Handling: Explore how to respond to user actions, like button clicks and text input.
- Logical Flow: Practice decision-making in code using conditional statements.
This project is a great starting point for students interested in:
- Developing interactive Python applications.
- Building simple chatbots with predefined logic.
- Understanding how GUIs work in Python.
By completing this project, students gain hands-on experience with Python programming and GUI development, laying the foundation for more advanced projects like intelligent chatbots, data visualization apps, and more!
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import scrolledtext
# Define the chatbot responses
chat_responses = {
"what is python?": "Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability.",
"who created python?": "Python was created by Guido van Rossum in 1991.",
"what are python's key features?": "Python features include easy syntax, dynamic typing, and extensive libraries.",
"what is tkinter?": "Tkinter is Python's standard library for creating graphical user interfaces.",
"how to define a function in python?": "Use the 'def' keyword followed by the function name and parentheses, e.g., def my_function():",
"what is a list in python?": "A list is a collection of ordered, mutable items, defined with square brackets, e.g., [1, 2, 3].",
"what is a tuple in python?": "A tuple is an immutable ordered collection of items, defined with parentheses, e.g., (1, 2, 3).",
"what is a dictionary in python?": "A dictionary is a collection of key-value pairs, defined with curly braces, e.g., {'key': 'value'}.",
"what is PEP 8?": "PEP 8 is the style guide for writing Python code.",
"what are python modules?": "Modules are files containing Python code that can be imported and reused.",
"what is a lambda function?": "A lambda function is an anonymous function defined using the lambda keyword.",
"what is list comprehension?": "List comprehension provides a concise way to create lists.",
"what are python decorators?": "Decorators are functions that modify other functions or methods.",
"what is the difference between python 2 and 3?": "Python 3 is the updated version with improved features and no backward compatibility.",
"what is __init__ in python?": "The __init__ method is the constructor method in Python classes.",
"what are python libraries?": "Libraries are collections of pre-written code for specific tasks, like NumPy and pandas.",
"what is the purpose of 'self' in python classes?": "'self' represents the instance of the class in its methods.",
"what is a python package?": "A package is a collection of modules, organized in directories.",
"what is a virtual environment in python?": "A virtual environment is an isolated environment for running Python applications.",
"what is python's GIL?": "GIL stands for Global Interpreter Lock, a mutex that protects access to Python objects.",
"what are python exceptions?": "Exceptions are errors detected during execution.",
"what is a python iterator?": "An iterator is an object that allows iteration over a collection.",
"what is the difference between is and == in python?": "'is' checks identity, '==' checks value equality.",
"what are python's data types?": "Python's data types include int, float, str, list, tuple, dict, etc.",
"what is the difference between list and array in python?": "Lists can store mixed data types; arrays are homogeneous.",
"how to handle exceptions in python?": "Use try-except blocks to handle exceptions.",
"what is the difference between deep copy and shallow copy?": "Deep copy duplicates objects, shallow copy references objects.",
"what is the use of pass in python?": "'pass' is a placeholder for future code.",
"what is python's range() function?": "range() generates a sequence of numbers.",
"what is the difference between break and continue in python?": "'break' exits loops; 'continue' skips to the next iteration.",
}
# Function to get chatbot response
def get_response(user_input):
return chat_responses.get(user_input.lower(), "I'm sorry, I don't know the answer to that question.")
# Function to handle sending messages
def send_message():
user_message = user_input.get()
chat_window.insert(tk.END, f"You: {user_message}\n")
user_input.delete(0, tk.END)
response = get_response(user_message)
chat_window.insert(tk.END, f"Bot: {response}\n")
# Create the main window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Upright AI Python Project Chatbot")
# Chat window
chat_window = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(root, width=50, height=20, wrap=tk.WORD)
chat_window.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=10)
chat_window.insert(tk.END, "Bot: Welcome to Upright AI Python Project Chatbot!\n")
# Input field
user_input = tk.Entry(root, width=40)
user_input.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
# Send button
send_button = tk.Button(root, text="Send", command=send_message)
send_button.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=10)
# Start the main event loop
root.mainloop()
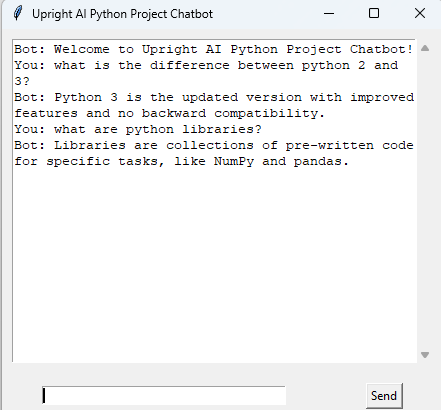
Output (Screenshot)